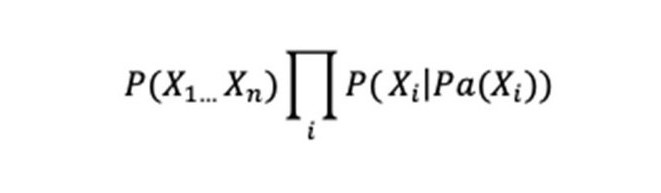An absolute point deductively measures using angle and distance in finite space and time. They are systems of measurement. With an absolute point and using the nonlinear visual sequence of a point to a line, then a triangle, then a square, and then a right angle, a causal model system can be created that has known values and probabilistic correlation. There are challenges of using systems of causation which give inclusion to particle matter, or points, in space and time. Systems can be represented by a baseball diamond and a soccer field positioned next to each other. It is possible to kick a soccer ball on the baseball diamond and vice versa to play catch on the soccer field. If individuals have a catch across the two fields, then entanglements are created. The baseball and mitt work perfectly fine on the soccer field, but they are not applicable to the game of soccer. Entanglements correlate systems but not in a probable way. A player would not score a point by throwing a baseball past the goalie. Moreover, non-locality addresses the problem of a causal system model that anchors to perceptual and physical object reality. An absolute point pinned to a sequence in finite physical space and time can be manipulated and controlled through interventionist method, which can then provide an outcome that makes sense.
A casual model system can be created with a coordinate graph, the Pythagorean Theorem, and the causal Markov condition.
Graph
The causal model system shows probabilistic correlation of angle and distance. The distance of hypotenuse shows probabilistic correlation to angle at 90, 180, and 270. The Pythagorean Theorem determines the hypotenuse with right angle at distance hn(5,10,15). Hypotenuse at 5(h1) divided by 90 equals v. Hypotenuse at 10(h2) divided by 180 equals v. Hypotenuse at 15(h3) divided by 270 equals v. Probabilistic correlation occurs at v.
If,
h1=7.071067811865475
h2=14.14213562373095
h3=21.213203435596426
then,
7.071067811865475/90=v
14.14213562373095/180=v
21.213203435596426/270=v
v=0.078567420131839
The probabilistic correlation is explained using the causal Markov condition:
P(7.071067811865475,14.14213562373095,21.213203435596426|Pa (90,180,270))
P/Pa=i
i=0.078567420131839
P(7.1,14.2,21.3|Pa (90,180,270))
i=0.078888888888889
0.078=0.08=0.1(0.02+)